3D-DOCTOR is being used by users around the world to create 3D visualization
and quantitative analysis using microscopy images.
The fully automatic and interactive image slice alignment functions will easily align scanned image slices for accurate 3D rendering and analysis.
Here are some image samples provided by researchers Lambot M-A, Mendive F,
Vanderhaeghen P, and Vassart G at IRIBHM, University of Brussels (ULB),
Brussels, Belgium. The research was done to confirm the anatomy of the
deferent ductules in mice, confirm how they fuse to make the epidydimis which is
believed to be different in mice and in humans.
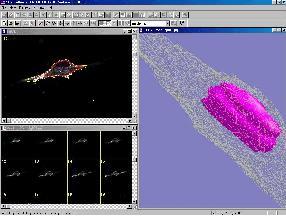
1. The screen image of the microscopic source images with scale
bar:
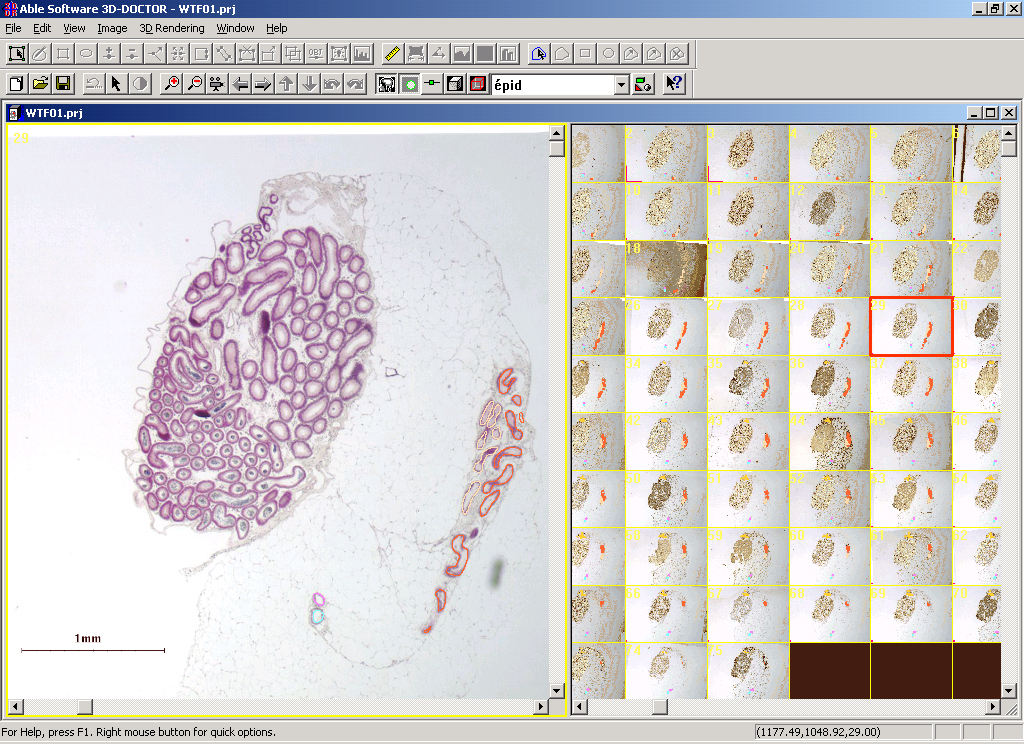
2. The whole mount view of a real dissected testis efferent ductules and
epididymis again with scale bar: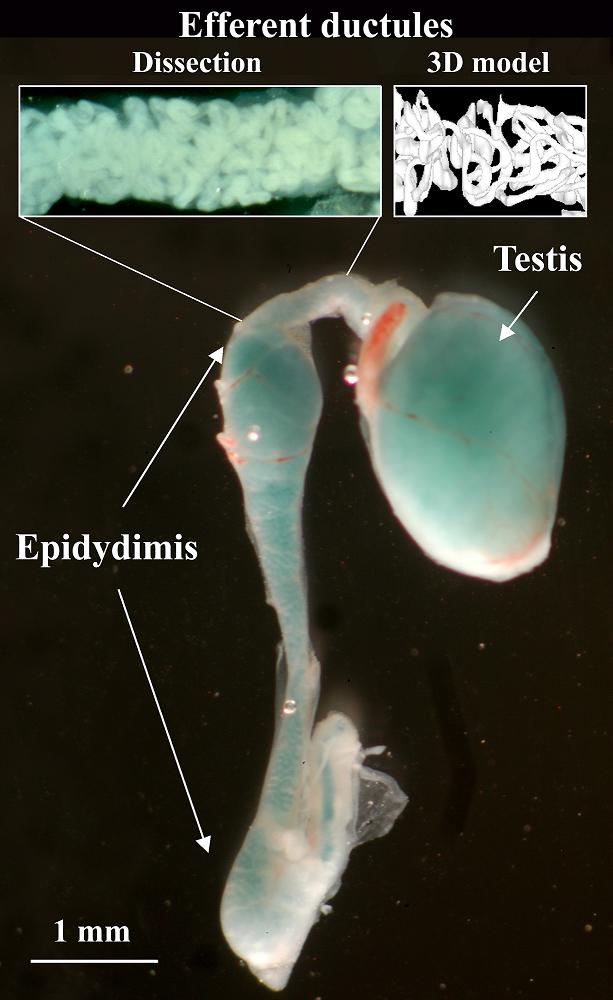
3. The 3D model of a single tube:
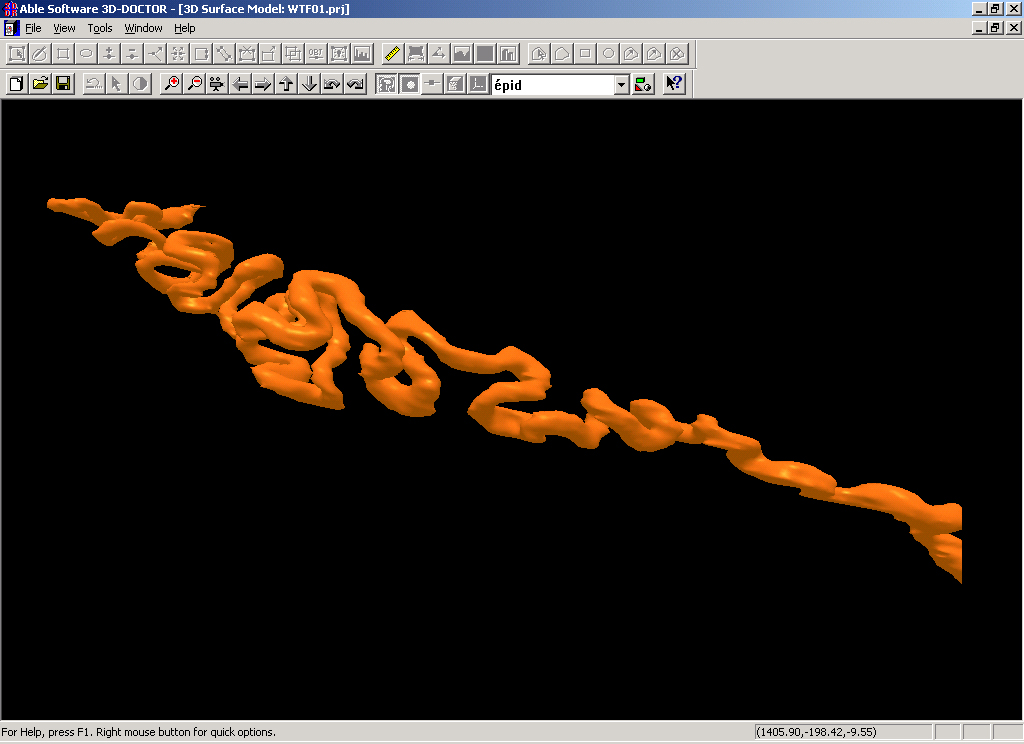
Other application samples:
 | 3D-DOCTOR is currently being used by many users
around the world for 2D and 3D microscopy imaging
applications, including SUNY Buffalo Microscopy
Imaging Center, Univ. of Minnesota, VA Medical
Center, and many others.
3D-DOCTOR is named the Top 3D Imaging Software by
Scientific Computing & Instrumentation
Magazine in the Year 2002 and 2000 Annual Technology
Leaders Issues. |
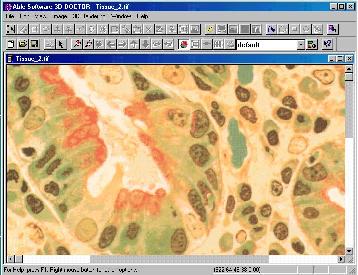
 | Bring 2D and 3D microscopy images in TIFF, BMP,
JPEG, DICOM, or raw file formats directly into
3D-DOCTOR for 3D display and analysis.
Create 3D models from microscopy images and
export the models to other systems for further analysis. Some 3D
export formats supported in 3D-DOCTOR are DXF for AutoCAD, 3DS for
3DStudio, STL for rapid prototyping, PLY (Polygon File) and VRML for
viewing on the Internet. |
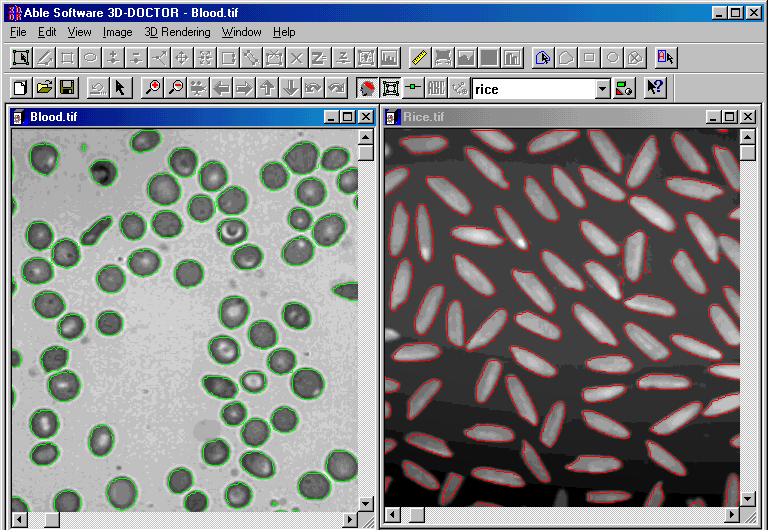 | Measurements: 3D volume, surface area, 2D area,
length, and a complete object report Automatic Image Segmentation: Creates object
boundaries automatically and produces a statistical report Automatic Image Slice Alignment Image Registration 3D-DOCTOR supports the industrial standard TWAIN
interface so your image acquisition can be done
easily. |
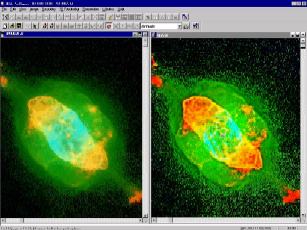
 | In-Focus Image Fusion: Creates a fully focused image from
multiple images of different focal planes. Color Image Fusion: Combine 3 grayscale images
into a 24-bit RGB image Mathematical Image Fusion: Used to combine two registered
images together using a user specified operator to create a new
fusion image. |
 | Maximum Entropy Based 3D Deconvolution Fast Nearest Neighbor Deconvolution |







