Reconstruction and Deconvolution
3D Volume Reconstruction Using Back-Projection and Iterative Method
3D-DOCTOR's Image/Reconstruction command takes a series of 2D images taken at angles with a constant interval and reconstructs the volume image using a filtered back-projection method or iterative reconstruction. If you have images acquired this way, you can create a 3D tomography image and perform 3D visualization and analysis using 3D-DOCTOR.
Advanced 3D Restoration by Deconvolution
3D-DOCTOR has implemented two types of 3D image deconvolution algorithms, a fast nearest neighbor algorithm and an optimal maximum entropy based iterative deconvolution. Image deconvolution is used to remove or reduce degradations that were incurred while the image was being obtained. These include the blurring introduced by optical systems and by image motion, as well as noise due to electronic and photometric sources.
When an image is acquired from a 3D imaging device such as microscope with a CCD camera and the PSF (point spread function of the device) image is available, a new 3D image can be created using 3D-DOCTOR's reconstruction function to deconvolve the acquired image with the system's PSF to remove the blur and distortion introduced in the imaging process. The deconvolution functions can be used by many applications where image restoration or reconstruction is required to improve the clarity and quality of the image.
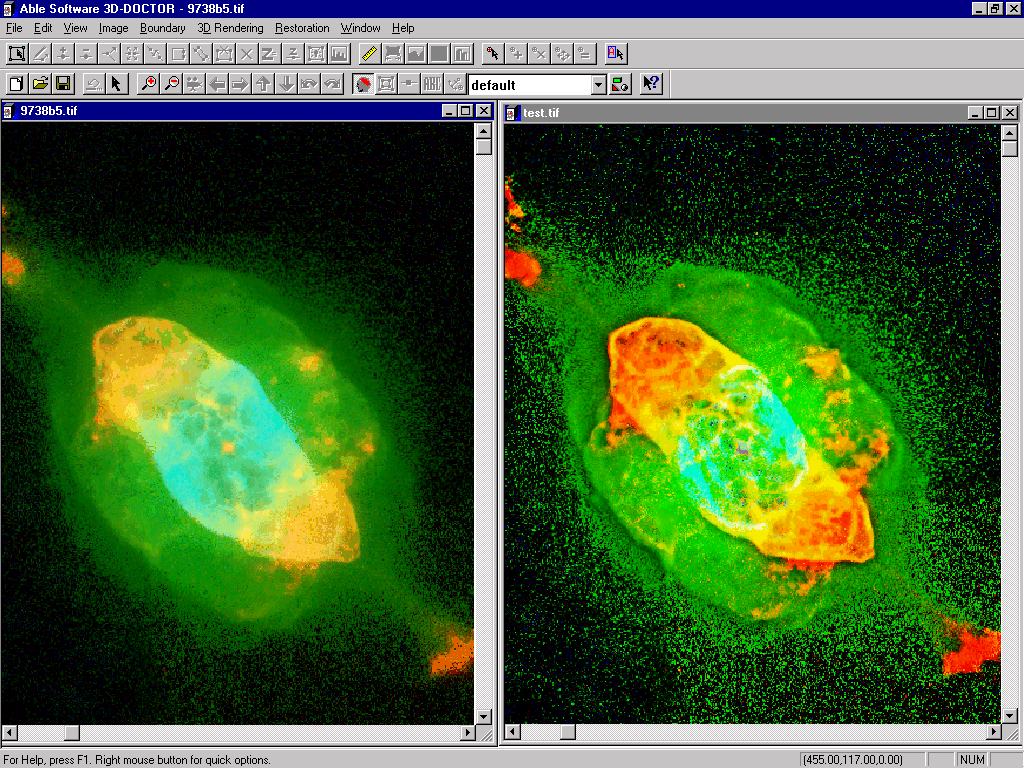
The following example shows an original Hubble Space Telescope image (left window) and the enhanced image (right window) using 3D-DOCTOR's Maximum Entropy based deconvolution algorithm. The difference between the two images is significant. All important details that are smeared in the original image can be seen much more clearly in the deconvolved image.
3D-DOCTOR makes it easy for you to apply the deconvolution functions to enhance your own images. This ensures that you will not miss any of the important details and that you will get more accurate information for your research. If you do not have a point spread function (PSF), 3D-DOCTOR has functions to create synthetic PSF for image deconvolution.
3D-DOCTOR provides the following 3-D deconvolution functions:
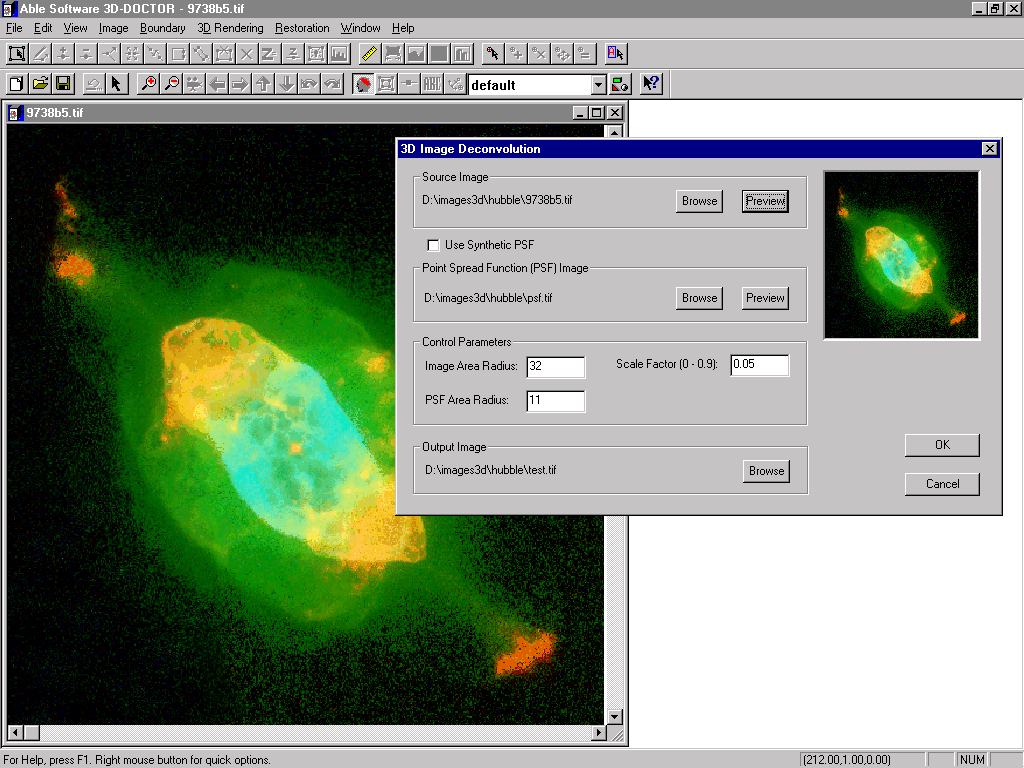
1. Fast Nearest Neighbor Deconvolution
This command performs a 3D image restoration or reconstruction using a Fast Nearest Neighbor deconvolution algorithm. The parameter dialog box requires the source image file name, the point spread function (PSF) image file name, and an output file name where the restored image is stored. Because this algorithm uses information from the nearest image layers, it deconvolves much faster than the Maximum Entropy method. When high restoration accuracy and quality is more important than speed, the Maximum Entropy method is highly recommended.
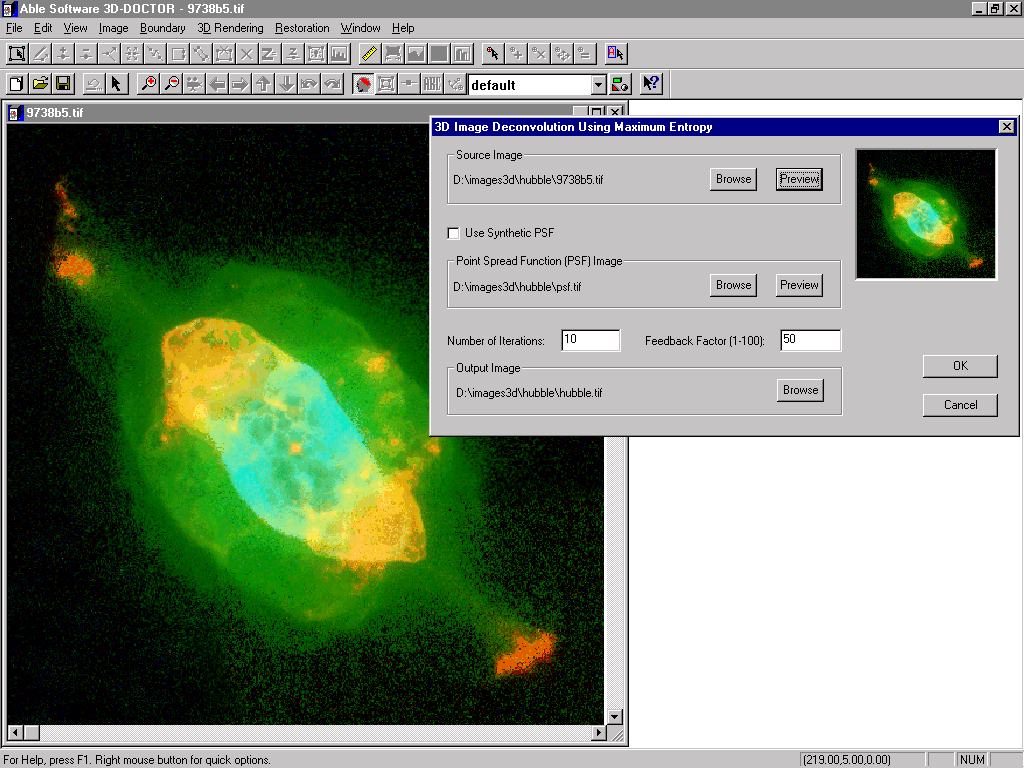
2. Maximum Entropy Deconvolution
This command performs a 3D image restoration or reconstruction using an Iterative Maximum Entropy deconvolution algorithm. The parameter dialog box requires the source image file name, the point spread function (PSF) image file name, an output file name where the restored image is stored, and the number of iterations. The larger the number of iterations, the longer the processing will take. Because this algorithm performs iterative deconvolution to get the highest restoration quality, it often takes longer processing time and more system memory usage than the Fast Nearest Neighbor deconvolution. Processing time also depends on the image size and your system setup.